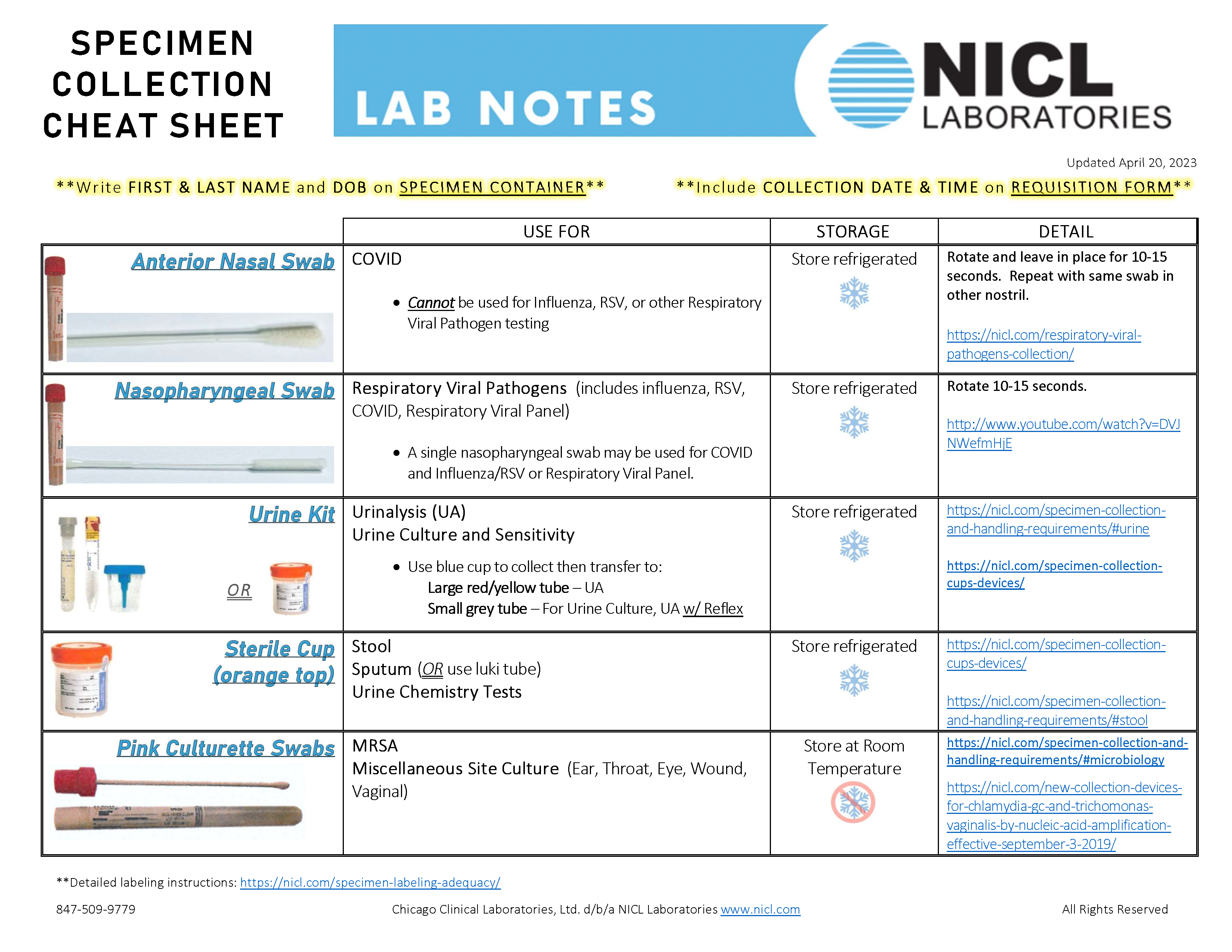
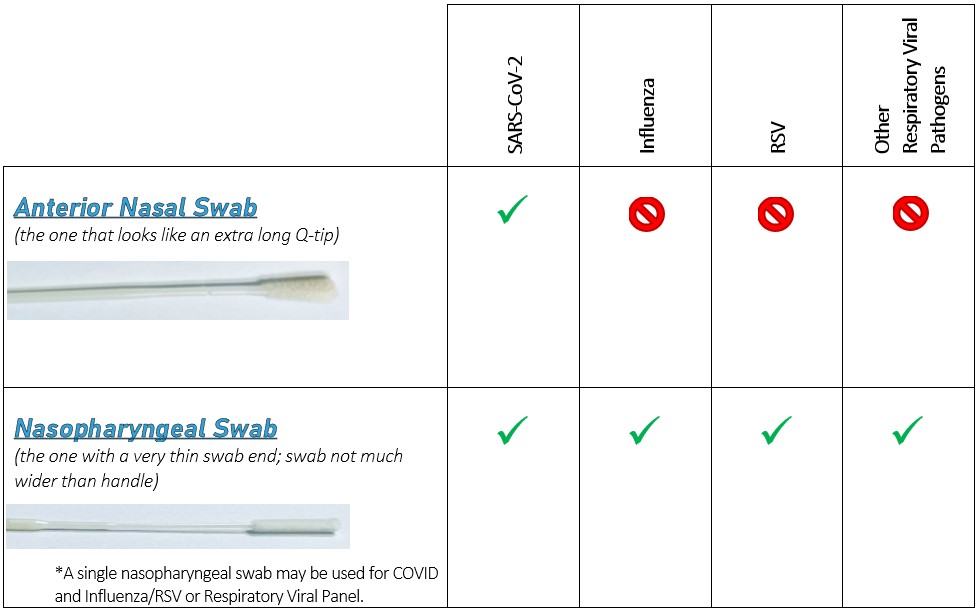
This document contains important information regarding test panels and profiles that you may order from or through NICL. Please be reminded that you should only order those tests which are medically necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of your patients and that ordering medically unnecessary tests that are billed to Medicare or Medicaid for reimbursement may subject you to civil penalties. You have the option to order all tests individually.
The attached table includes the panel order codes, the individual components, CPT codes[1] and names, and the 2025 Medicare reimbursement rates for currently offered Organ and Disease Panels.
r
| Order Code | CPT Name | CPT[1] | Components Included | 2025 Medicare Reimbursement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20004 | Electrolyte Panel | 80051 | Sodium Potassium Chloride, Carbon Dioxide | $7.01 |
| 20167 | Hepatic Function Panel | 80076 | Total Protein, Albumin, Total Bilirubin, Direct Bilirubin, Akaline Phosphatase, AST, ALT | $8.17 |
| 20163 | Basic Metabolic Panel | 80048 | Glucose, Urea Nitrogen, Creatinine, Sodium, Potassium, Chloride, Carbon Dioxide, Calcium | $8.46 |
| 20165 | Renal Function Panel | 80069 | Albumin, Calcium, Carbon Dioxide, Chloride, Creatinine, Glucose, Phosphorus, Potassium, Sodium, Urea Nitrogen | $8.68 |
| 20164 | Comprehensive Metabolic Panel | 80053 | Glucose, Urea Nitrogen, Creatinine, Solium, Potassium, Chloride, Carbon Dioxide, Calcium, Total Protein, Albumin, Total Bilirubin, Alkaline, Phosphatase, AST, ALT | $10.56 |
| 20062 | Lipid Panel | 20062 | Triglycerides, Total Cholesterol, HDL Cholesterol | $13.39 |
| 84165 | Protein Elect. & Total | 84155 1 84165 1 | Protein Protein Electroph Serum | $3.67 $10.74 |
| 86325 | Immunofixation Eval Serum | 84155 1 84165 1 | Protein Protein Electroph Serum | $3.67 $10.74 |
| 84141 | Primidone (Mysoline®) | 80184 1 80188 1 | Phenobarbital Primidone | $15.30 $16.59 |
| 84080 | Alkaline Phosphatase ISO | 84075 1 84080 1 | Alk Phosphatase Alk Phosphatase, ISO | $5.18 $14.78 |
[1] The CPT codes and related information provided are based on AMA guidelines and are for informational purposes only. CPT coding is the sole responsibility of the billing party. Please direct any questions regarding code to the payer being billed.